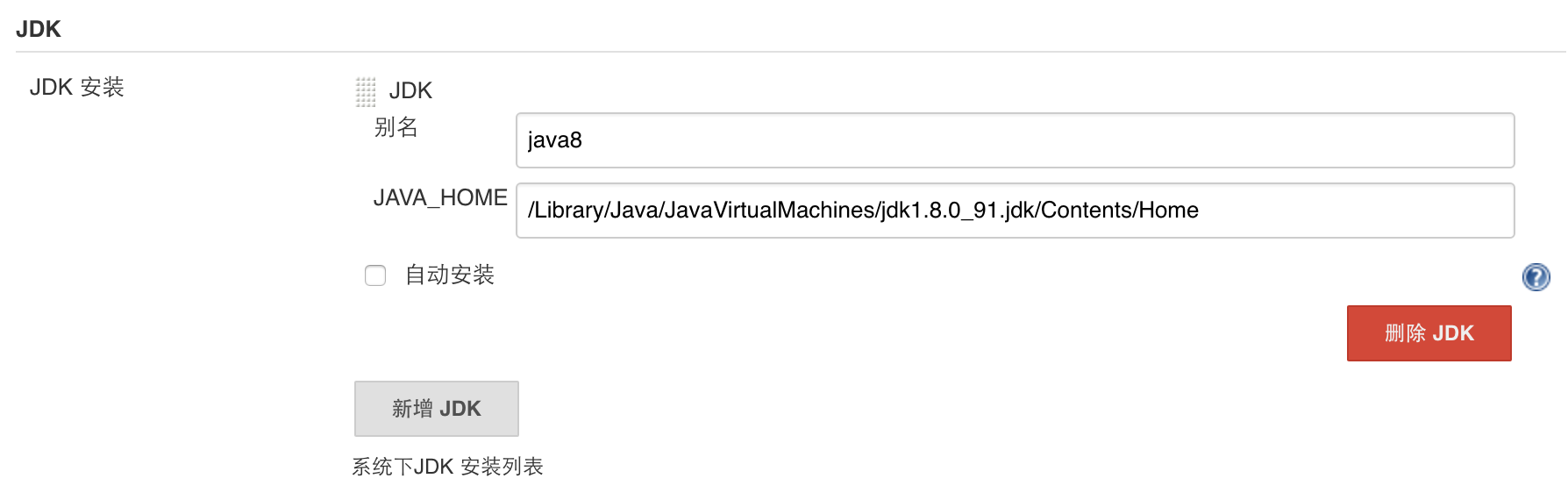
dubbo对spring的标签的扩展
<dubbo:application name="${dubbo.application.name}" owner="whx" organization="whx-inc"/>
<dubbo:registry protocol="zookeeper"
address="${dubbo.registry.address}"
group="${dubbo.registry.group}"
file="${dubbo.registry.file}"/>
<dubbo:annotation package="com.whx"/>
<dubbo:consumer check="false" retries="0"/>
<dubbo:provider threads="600" threadpool="fixed" retries="0" loadbalance="roundrobin" accesslog="true"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="${dubbo.protocol.dubbo.port}" charset="utf-8"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="hessian" port="${jetty.port}" server="jetty" accesslog="true"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="rest" port="${dubbo.protocol.rest.port}"
keepalive="true" server="netty"
extension="com.whx.common.rest.FastJsonProvider,com.whx.common.rest.JsonExceptionMapper" />
<context:property-placeholder
ignore-resource-not-found="false"
location="classpath*:application.properties,classpath*:redis.properties,classpath*:dubbo.properties,classpath*:kestrel.properties,classpath*:db.properties" />
<dubbo:monitor address="${dubbo.monitor.address}" />
这些注解其实都是对spring标签的扩展,由spring的api扩展出来,方便我们不去读取xml,直接通过标签的方式加载为bean对象
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
}
}
spring schema扩展实现
1.编写Bean类,此为业务类
public class People {
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.编写xsd文件 xsd文件中包含了Bean类的属性映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema
xmlns="http://whx4j8.github.io/people"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
targetNamespace="http://whx4j8.github.io/people"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"/>
<xsd:element name="people">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:attribute name="age" type="xsd:int"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>
element name=”people” 代表people,spring会通过其内的配置项xsd:attribute在xml提示字段,类似xml提示
xmlns targetNamespace 代表对应的唯一命名空间
一般将xsd放到META-INF下
3.编写NamespaceHandler 和 spring.schemas 映射配置文件
registerBeanDefinitionParser(“people”, new PeopleBeanDefinitionParser());
当读取到people这个节点名时,使用PeopleBeanDefinitionParser类去解析,而不是仅仅将字段注入属性中。
public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("people", new PeopleBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
PeopleBeanDefinitionParser通过反射将xml中配置的值注入到生成的bean对象中。
public class PeopleBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return People.class;
}
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
String name = element.getAttribute("name");
String age = element.getAttribute("age");
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(name)){
builder.addPropertyValue("name",name);
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(age)){
builder.addPropertyValue("age",age);
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(id)){
builder.addPropertyValue("id",id);
}
}
}
4.spring.handlers 和 spring.schemas
现在xml规范有了,xml解析器也有了,Bean对象也有了。
spring.handlers文件
http\://whx4j8.github.io/people=com.whx.spring.MyNamespaceHandler
告诉spring当使用http\://whx4j8.github.io/people使用com.whx.spring.MyNamespaceHandler去配置解析
spring.schemas文件
http\://whx4j8.github.io/people.xsd=META-INF/people.xsd
告诉spring去加载那些xsd文件
5.application.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:whx="http://whx4j8.github.io/people"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://whx4j8.github.io/people
http://whx4j8.github.io/people.xsd">
<whx:people id="people" name="whx" age="22"></whx:people>
</beans>
xmlns:whx=”http://whx4j8.github.io/people“ 为该schema命名为whx,在下面的xml直接使用whx即可
6.使用
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
People people = (People) ctx.getBean("people");
System.out.println(people.toString());
}
输出People{id=’people’, name=’whx’, age=22}
参考
dubbo源码解析